By Miriam King, Devon Kristiansen, and Anna Bolgrien
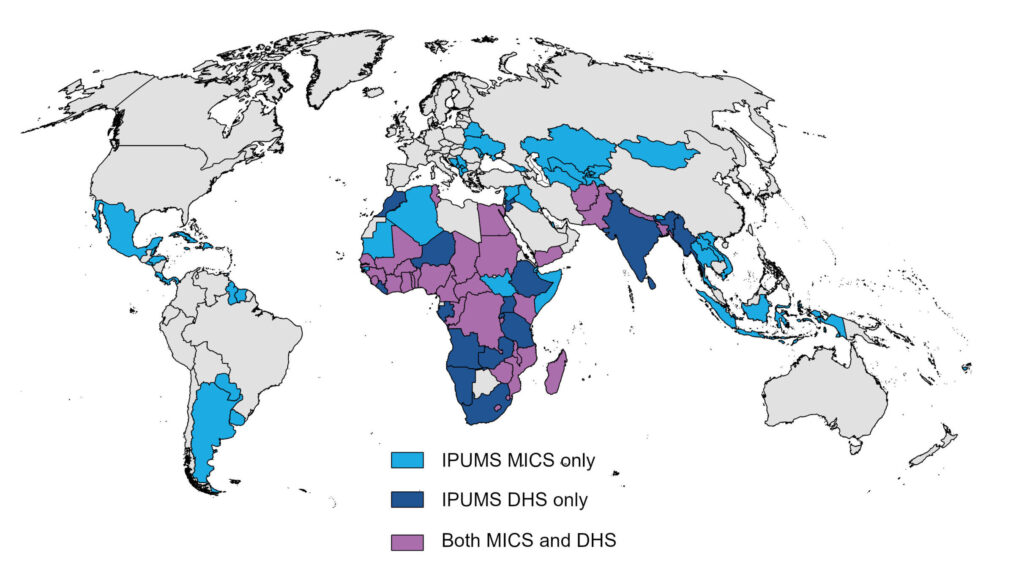
IPUMS Global Health includes integrated data from three international health surveys: Demographic and Health Surveys (IPUMS DHS), Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (IPUMS MICS), and Performance Monitoring for Action (IPUMS PMA). All three surveys are nationally representative, primarily focus on low- and middle-income countries, and address issues related to the health and well-being of women and young children. These commonalities make combining integrated data across these data collections appealing. As Figure 1 shows, IPUMS DHS and IPUMS MICS cover different countries; combining them extends the geographic coverage of harmonized versions of data covering similar topics. Researchers can also combine data for those countries included in both IPUMS DHS and IPUMS MICS to provide additional observation points for time-series analyses.
Figure 1: Countries covered by IPUMS DHS and IPUMS MICS
Researchers who want to carry out cross-survey analyses face practical challenges. IPUMS imposes consistent variable names and codes within one kind of survey (DHS, MICS, or PMA); harmonized variable names and codes differ between these surveys. On each project’s website, the documentation for each variable highlights comparability issues to keep in mind when combining multiple samples, either within one type of survey or across survey types. IPUMS users must make separate customized data files from each database and merge those files. And subtle differences in question wording, skip patterns, geographic boundaries, and sampling procedures—such as MICS’ taking reports on child health from caretakers other than the biological mother—can introduce inconsistencies and inadvertent errors.