By Shine Min Thant
Qatar, a small yet influential state in the Middle East, is a very interesting case study for demographic research because of its rapid development over the past thirty years. Qatar occupies a peninsula only slightly larger than the U.S. state of Rhode Island that juts out into the Persian Gulf from its border with Saudi Arabia. The country has experienced relatively rapid economic growth since the late 20th century, mainly due to its vast reserves of natural gas and oil. This newfound wealth allowed Qatar to invest heavily in its healthcare, infrastructure, and education – therefore making the country an ideal case study for social change and development. Additionally, a recent surge in Qatar’s immigrant population (which constitutes over 78 percent of the population) also makes it an ideal country to study social mobility and social change.
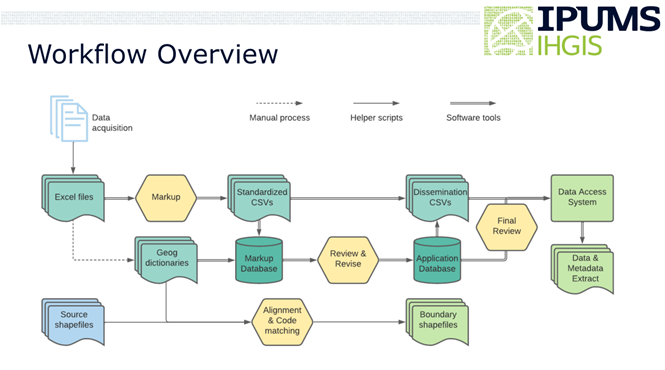
As part of the ISRDI Diversity Fellowship Program, I worked with Dr. Tracy Kugler, Professor Steven Manson, Professor Evan Roberts, and undergraduate student Rawan AlGahtani on a project to examine Qatar’s change using census data from 1984, 1997, and 2004. Summary tables from all three censuses were previously only available as printed documents. As a first step, we needed to transform the data from a hard-to-get printed format to widely accessible IPUMS IHGIS format. This process included multiple steps from conducting optical character recognition (OCR) to conducting data quality checks using R scripts (Figure 1).