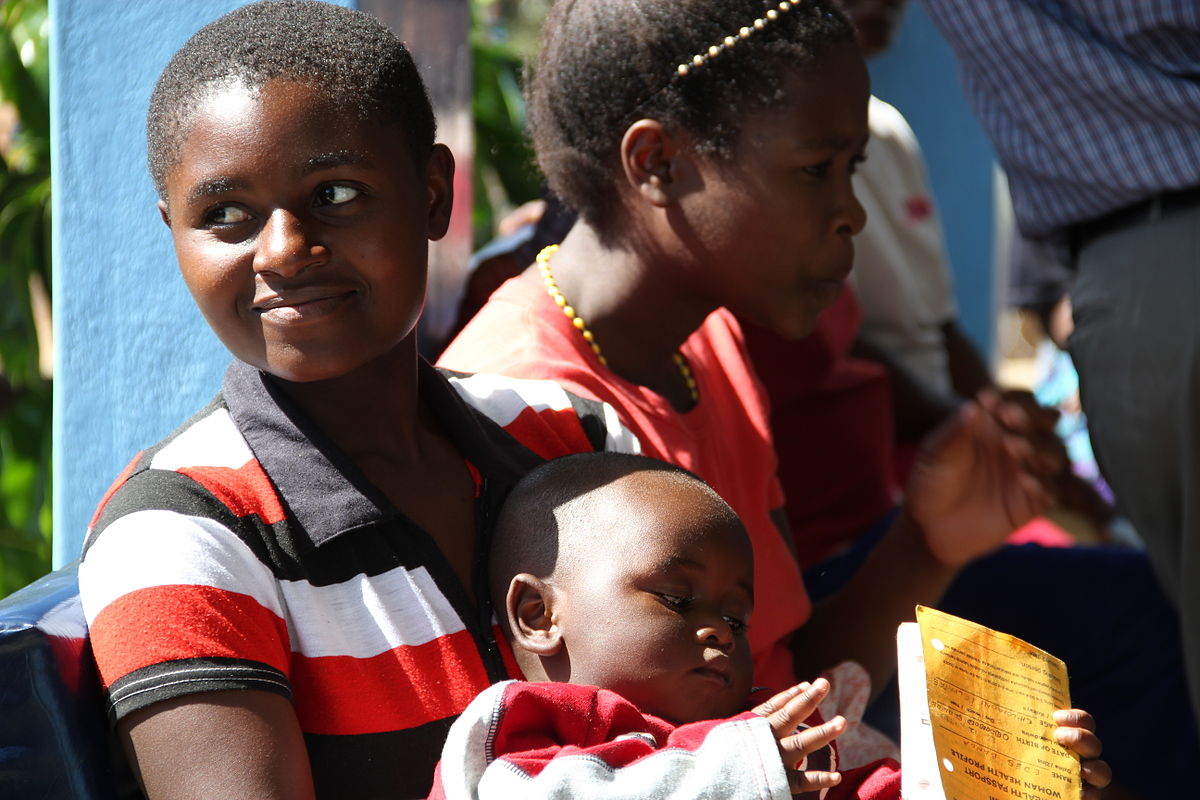
As of May 2016, IPUMS-DHS includes over 2000 integrated variables from 90 Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) in 21 countries, and allows researchers to select women, children, or births as their unit of analysis.
This year, IPUMS-DHS added data from 12 surveys from three new countries, Cameroon, Madagascar, and Rwanda, along with the latest samples from Egypt and Zambia. The previous two data releases covered Benin, Burkina Faso, Cote d’Ivoire, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, India, Kenya, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Because all countries included have conducted at least three DHS surveys, dating back as early as the late 1980s, the data are well-suited to studying dramatic change over time as well as differences between countries.
Most of the information collected in the Demographic and Health Series is provided by female respondents of childbearing age. Many of the questions relate to the woman herself, such as her education, media exposure, marital history, contraceptive knowledge and use, family size desires, experience of domestic violence, and knowledge about illnesses such as HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and fistula. Other questions relate to the health of the woman’s children under age five, such as antenatal and delivery care, nutrition, vaccinations, and recent diarrheal and respiratory illnesses and treatment. The 2016 release adds new child anthropometric variables such as height, weight, and BMI. Finally, a limited amount of information, such as sex and survival status, is collected for up to 20 births per woman.
Choosing young children or births as the unit of analysis provides immediate access to information about their mothers. Available topics relating to the child’s mother include her background characteristics (such as education, religion, and ethnicity), marriage and work history, beliefs about appropriate treatment of childhood illnesses, barriers to healthcare access, household decision-making, family size desires and family planning use, tobacco use, insurance coverage, and knowledge about tuberculosis and fistula.
New geographic variables identifying major administrative units in IPUMS-DHS are now available to match those in IPUMS-International census data. The spatially-consistent variables in the two databases allow researchers to summarize census data and attach it as contextual information to the DHS samples or vice versa.
The 30-year period covered by the Demographic and Health Surveys has been marked by extensive changes in Africa. For example, the total fertility rate in Sub-Saharan Africa fell from 6.3 children in 1990 to 4.9 in 2010, and women’s access to primary schooling has increased dramatically. At the same time, many issues related to women’s and children’s health persist, such as a “stall” in the region’s demographic transition, high levels of female genital cutting and intimate partner violence, and endemic diseases (e.g., malaria, child diarrhea, AIDS).
With over 2000 variables, 90 samples, and 21 countries included, IPUMS-DHS now supports research on these and many other topics, for India, Egypt, and much of Sub-Saharan Africa.
IPUMS-DHS is created at the Minnesota Population Center and is made possible through funding from the National Institute for Child Health and Human Development. Survey data included in IPUMS-DHS come from The DHS Program, with funding from USAID and collaboration between ICF International and participating countries